Every year between 50 and 100 million cases of dengue occur in the world, a tropical disease that causes a state of general affectation so intense that it is known as breakbone fever. Know its symptoms and treatment.
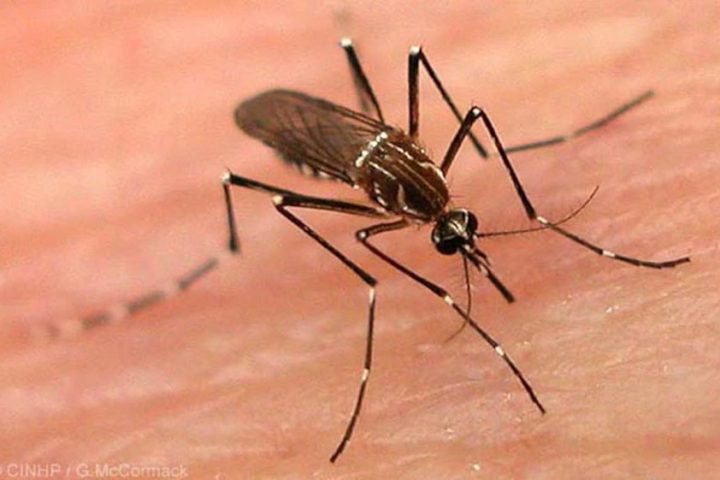
Dengue is an infectious viral disease considered a tropical disease. It is transmitted by the bite of a female hematophagous mosquito (which feeds on blood), popularly known as the white-legged mosquito, and whose scientific name is Aedes aegypti.
This mosquito lives mainly in urban habitats and fulfills part of its life cycle in artificial water reservoirs such as vases, ponds, abandoned tires, etc. It stings the man mainly during the day, although it can also do it at night if a light is left on inside the house.
There are other types of Aedes mosquitoes capable of transmitting the virus, although less efficiently. The most important of them comes from Asia and is called Aedes albopictus, also known as the tiger mosquito. This mosquito has adapted to living in colder climates than Aedes aegypti, so it can be found outside the tropics in many European countries, the United States, and Canada.
There are four serotypes of dengue virus designated with the abbreviations DEN-1, DEN-2, DEN-3, and DEN-4 that are the cause of two types of clinical pictures: dengue fever, which is the usual clinical picture, previously known as classic dengue; and dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue hemorrhagic fever, which is less common but much more serious.
The World Health Organization prefers that dengue hemorrhagic fever be known as severe dengue. Patients infected with one of the four serotypes of the virus are immunized against this type of dengue, but only temporarily (about 2-12 months) against the other three. In fact, there is a higher risk of developing dengue hemorrhagic fever if a new episode of dengue occurs due to a different serotype than the first one.
The febrile syndrome caused by dengue virus infection is usually of variable severity, and the general condition is often so severe that it is also known as break-bone fever.
Prevalence and affected regions
From an epidemiological point of view, the main regions where this infection is found are countries in Latin America and Southeast Asia. However, there are also many cases in Africa, some areas of Arabia, the South Pacific, Puerto Rico, and other tropical regions and subtropical.
According to data from the Society for Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, more than 70% of the dengue disease burden is concentrated in South-East Asia and the Western Pacific.
According to WHO data, 40% of the world is at risk of contracting dengue. It is estimated that there are between 50 and 100 million cases of dengue per year in the world. However, dengue is a very little-known infection in the United States or Europe.
In these regions, imported cases are usually diagnosed in travelers from tropical regions. However, autochthonous cases have already been described in European countries such as France or Croatia, probably transmitted by Aedes albopictus (tiger mosquito).